Parental Participation in Education can Enhance Performance of Children
Parental involvement in child's education has positive impact. Many psychologists and educational theorists recognized the significance of parental involvement in education.
Parental involvement in school is described as parent reported participation at least once during the school year in attending a general school meeting; attending a scheduled meeting with their child's teacher; attending a school event; or volunteering in the school or serving on a school committee.
It is stated by psychologists that students with parents who are involved in their school tend to have less behavioural problems and good academic record, and are more likely to complete high school as compared to students whose parents are not involved in their school. Positive effects of parental involvement have been established at both the elementary and secondary levels across several studies, with the largest effects often occurring at the elementary level.
Many researchers have observed that parent's active role in education of child enhances the performance of students and improve their life. Susan Jarmuz-Smith, Rounds, and Gorney (1992) found that parental engagement positively affects child's learning. Jarmuz-Smith considered that overall, the key to parent involvement is providing meaningful engagement opportunities that offer concrete ways for parents to build knowledge of and the capacity to involve themselves in the educational system. If we ask parents to help, research shows they will.
Figure : Model of parent's involvement in child's education
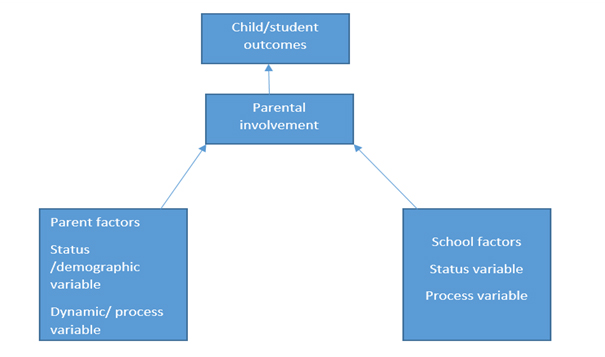
According to Academic Joyce L. Epstein, The evidence is clear that parental encouragement, activities and interest at home, and parental participation in schools and classrooms positively influence achievement, even after the students' ability and family socio-economic status are taken into account.
Parental participation in education of child allows them to monitor school and classroom activities, and to synchronize their efforts with teachers to inspire acceptable classroom behaviour and make certain that the child completes schoolwork. Teachers of students with highly involved parents tend to give greater attention to those students. Parents who involve in child's study are more likely to recognize at earlier stages problems that might impede student learning. Parental involvement in school, and positive parent-teacher interactions, have also been found to positively affect teacher's self-perception and job pleasure.
Researcher, Reuven Feuerstein conveyed that good communication from a school certainly increases parent participation. He clarified: Just the small act of communicating with parents about the needs of the school motivated parents to become involved.
Joyce Epstein, described that there are six different types of parental involvement.
These areas are as under
1. Divining information about student improvement and opening up a pathway for parents to communicate with schools
2. Providing information to parents about child development and age-appropriate expectations.
3. Boosting volunteering to fit in with parents' schedule.
4. Ideas and policies for parents to assist in homework of child.
5. A two-way connection between community, business and schools.
6. Serving parents to become involved in organizations, committees and school boards.
In the decade of 1980s, there were educational reforms in American parents and their active role in governing schools, in receiving information and in gaining the right to state a preference for a specific school made positive changes in learning of students.
Parental involvement in school is measured by attendance at a general meeting, a meeting with a teacher, or a school event, or by volunteering or serving on a committee. Parents who are highly educated are more likely to be involved in their children's schools.
It is found in many experimental researches that increasing parental involvement in school can be challenging, particularly when the families are economically underprivileged, or do not have English as their primary language.Low-income parents' involvement in school may be delayed by transportation problems, chronic health conditions, or conflicts with work schedules, while parents whose primary language is not English may hesitate to contribute in school activities, or may belong to a culture where questioning teachers is not a norm.
Many schools have adopted several strategies to increase parental involvement in school, that range from extensive promotion of events such as back to school nights, to school-based cultural events in areas with large refugee populations.Large-scale initiatives, such as the community schools movement, are also designed to increase disadvantaged families' involvement in school by making the school a hub of social services for the neighborhood. Though, some studies have thoroughly assessed the effects of such programs on parental involvement.
It is well understood by general public that parental support is significant way to improve the child's academic performance. Lack of parental involvement is the major problem facing public schools. Extensive researches from past indicated that when parents are involved students have higher grades, test scores, and graduation rates, better school attendance,increased motivation, better self-esteem, lower rates of suspension, less use of drugs and alcohol and minor incidents of school violence.
For More Articles: click Here